Understanding Linked List in Python
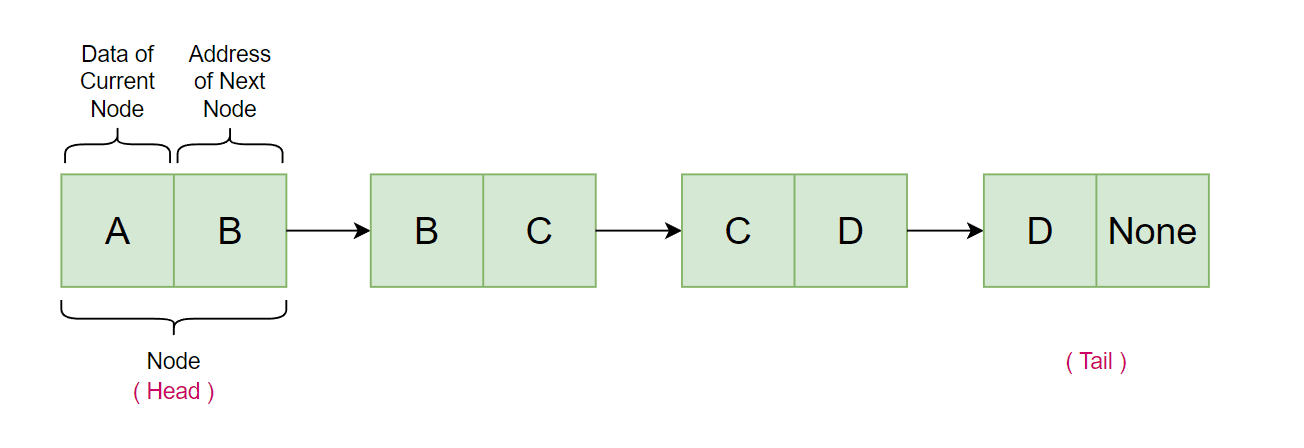
In the realm of data structures, the linked list stands out as a flexible and efficient way to store and manage data. Unlike arrays, linked lists are not constrained by a fixed size and offer efficient insertions and deletions. Let's unwrap the concept of linked lists and see how we can implement one in Python.
What is a Linked List?
A linked list is a collection of elements called nodes, each containing two main elements: data and a reference to the next node. The starting node is known as the "head," and the ending point is indicated by a node that points to None, which is called the "tail."
The Node: Building Block of a Linked List
The basic building block of a linked list is the node. Here's a simple node class in Python:
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.next = None def __str__(self):
return f"Data: {self.data}"Each Node instance holds some data and a pointer, next, which points to the next node in the list. The __str__ method is defined for easy debugging and visualization of the node’s content
Crafting the Linked List Class
Now, let's construct our linked list class:
class LinkedList:
def __init__(self):
self.head = None self.tail = None def append(self, node: Node):
if not self.head:
self.head = self.tail = node
else:
self.tail.next = node
self.tail = node
def prepend(self, node: Node):
if not self.head:
self.head = self.tail = node
else:
node.next = self.head
self.head = nodeOur LinkedList class maintains references to the head and tail nodes. When we append a node, we simply adjust the next reference of the current tail node and update the tail to the new node. To prepend, we set the new node’s next reference to the current head and then update the head.
Using the LinkedList Class
With our Node and LinkedList classes ready, we can create a linked list and populate it:
if __name__ == "__main__":
linked_list = LinkedList()
linked_list.append(Node('A'))
linked_list.append(Node('B'))
linked_list.append(Node('C'))
linked_list.append(Node('D'))
item = linked_list.head
while item:
print(f"Current Data: {item.data}")
item = item.nextOutput:
Current Data: A, Next Data: B
Current Data: B, Next Data: C
Current Data: C, Next Data: D
Current Data: D, Next Data: NoneThis code snippet creates a linked list and appends several nodes. It then traverses the list, starting from the head, and prints out each node’s data until it reaches the end of the list.
Conclusion
Linked lists are a fundamental data structure that provide an efficient way to store and manipulate collections of data. They are especially useful when you need constant-time insertions and deletions, as they do not require the shifting of elements like in an array.
The beauty of a linked list lies in its simplicity and the elegance of its nodes being linked together. By mastering linked lists, you unlock a new level of data structure sophistication that can be applied to various complex problems in computer science.
Stay tuned for our next blog post where we will explore the intriguing process of reversing a linked list, which is not only a common interview question but also a great exercise in understanding the intricacies of pointer manipulation.
Please visit the github repo for entire code. Thank You
niranjanblank
https://github.com/niranjanblank/Data_Structures/blob/master/LinkedList/LinkedList.py